Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibata, Kaoru
Hamon, 28(1), p.26 - 28, 2018/02
We briefly introduce the pedigree of the backscattering neutron spectrometer and the specification of DNA; a time-of-flight (TOF) type near-backscattering spectrometer (n-BSS), with Si crystal analyzers which was constructed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC).
Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Tsujimura, Norio; Okada, Kazuhiko
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 11, p.070009_1 - 070009_6, 2016/11
Beta spectra of various nuclide species were measured by commercially available compact spectrometer. The shape of spectra obtained from the spectrometer approximately agreed with that of theoretical spectra. The beta dose equivalent at any depths has been able to be obtained as a product of measured pulse height spectra and appropriate conversion coefficients of ICRP Publ. 74. The dose rates evaluated from the spectra were comparable to the reference dose rates of standard beta calibration sources. And, we were able to determine the dose equivalent with relative error of indication of 10% without the complicated correction.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2016-005, 40 Pages, 2016/05
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) method is an attractive technique because real-time, in-situ and remote elemental analysis is possible without any sample preparation. The LIBS technique can be applied for analyzing elemental composition of samples under severe environments such as the estimation of impurities in the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the detection of fuel debris in the post-accident nuclear core reactor of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For applying LIBS to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is indispensable to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). In the present study, an echelle spectrometer with a resolving power of 50,000 was employed to identify spectra of natural uranium of wavelength ranging from 470 to 670 nm. The 173 atomic spectra and 119 ionic spectra can be identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2015-012, 48 Pages, 2015/10
It is important to analyze the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the fuel debris generated at the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Therefore, the remote analysis for nuclear fuel materials using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) is studied. For applying Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is very important to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). Then, the high resolution spectra of natural uranium of wavelength region of 350-470 nm are measured using LIBS, 247 atomic spectra and 294 single ion spectra were identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
 Ge spectrometer
Ge spectrometerKoizumi, Mitsuo; Osa, Akihiko; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Mizumoto, Motoharu; Oshima, Masumi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Osaki, Toshiro*; Harada, Hideo*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 562(2), p.767 - 770, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)In order to measure the neutron capture cross section of minor actinides, we have proposed the use of a 4 Ge spectrometer. A Time-of-Flight neutron beam line for the experiment has been constructed at the KURRI electron LINAC. The assembling of the 4
Ge spectrometer. A Time-of-Flight neutron beam line for the experiment has been constructed at the KURRI electron LINAC. The assembling of the 4 Ge spectrometer is in progress. We are also developing a new data acquisition system based on a digital processing technique.
Ge spectrometer is in progress. We are also developing a new data acquisition system based on a digital processing technique.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Wu, G.*; Kitajima, Yoshinori*
Surface Science, 593(1-3), p.310 - 317, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.64(Chemistry, Physical)Using a newly developed rotatable time-of-flight mass spectrometer(R-TOF-MS) and polarized synchrotron radiation, orientation effect on fragmentation and desorption pathways occurring at the top-most layers of molecular solids have been investigated. Reported will be polarization-angle dependencies of TOF mass spectra, high-resolution electron- and ion-NEXAFS in condensed chlorobenzene.
Ikeura, Hiromi*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Shimada, Hiromichi*
Surface Science, 593(1-3), p.303 - 309, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.1(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Saegusa, Jun; Yoshizawa, Michio; Yoshida, Makoto
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 547(2-3), p.592 - 600, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.8(Instruments & Instrumentation)The moderator structure of a neutron spectrometer was optimized with a Monte Carlo code of MCNP-4B. The spectrometer consists of a cylindrical moderator and a position-sensitive thermal neutron detector. It can obtain an energy spectrum from thermal neutron distribution along the cylindrical axis of the moderator. The structure of the moderator was improved by putting a low hydrogen density material in the front of a high hydrogen density one and inserting a neutron absorber which eliminated thermal neutrons diffusing in the moderator. These improvements make energy resolution of the spectrometer better especially for the low energy neutrons from a few tens to 100 keV. The designed spectrometer can be applied to the measurement of energy spectrum over a neutron energy range from a few keV to 20 MeV.
Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Oishi, Tetsuya*; Yamasoto, Kotaro; Yoshida, Makoto
JAERI-Research 2004-021, 43 Pages, 2004/12
We have designed and developed a  measurement system to certify radioactive wastes below the clearance level. By advancing non-destructive
measurement system to certify radioactive wastes below the clearance level. By advancing non-destructive  -ray assay technology, it aims at quantitative determination of radionuclides contained in 200 litter drum/container wastes. Unlike the waste from a nuclear power plant, you have to assume that the waste originating from radioisotope usage and nuclear research laboratory have a variety of contents and a complex mixture of radionuclides, and furthermore the uniformity of activity concentration is unknown. To cope with the problems, we have developed the
-ray assay technology, it aims at quantitative determination of radionuclides contained in 200 litter drum/container wastes. Unlike the waste from a nuclear power plant, you have to assume that the waste originating from radioisotope usage and nuclear research laboratory have a variety of contents and a complex mixture of radionuclides, and furthermore the uniformity of activity concentration is unknown. To cope with the problems, we have developed the  -ray measuring instruments (units) with effective improvement of capability against each problem. They are (1) germanium
-ray measuring instruments (units) with effective improvement of capability against each problem. They are (1) germanium  spectrometry unit for enhanced peak identification, (2) positioning detection unit for positioning of
spectrometry unit for enhanced peak identification, (2) positioning detection unit for positioning of  interactions and (3)high-efficiency detection unit for separation of low-energy component. This report summarizes the direction of the clearance level measuring system and the three developed measuring units with their performances.
interactions and (3)high-efficiency detection unit for separation of low-energy component. This report summarizes the direction of the clearance level measuring system and the three developed measuring units with their performances.
Nishitani, Takeo; Osakabe, Masaki*; Shinohara, Koji; Ishikawa, Masao
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(10), p.860 - 869, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Kaoru; Tamura, Itaru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi; Middendorf, H. D.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 1, p.351 - 354, 2003/07
In this research report we describe the design of DYANA, a new neutron spectrometer dedicated for biology, biomaterials, and related soft-matter studies, which will be installed in the material and life science experimental facility project at the JAERI Tokai establishment. The DYANA spectrometer is an indirect-geometry crystal-analyzer instrument and its energy and momentum transfer range are from several 10 eV to several meV and from 0.1
eV to several meV and from 0.1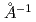 to several
to several 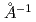 , respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
, respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
Tamura, Itaru; Aizawa, Kazuya; Harada, Masahide; Shibata, Kaoru; Maekawa, Fujio; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 1, p.529 - 539, 2003/07
Moderator components of the McStas code have been created for the design of the spectrometers of JSNS. Three cryogenic moderators are adopted in JSNS, One is a coupled H moderator for high intensity experiments and other two are decoupled H
moderator for high intensity experiments and other two are decoupled H with poisoned or unpoisoned for high resolution moderators. Monte Carlo simulations have turned out to be useful for design of neutron scattering instruments with high complexity. The software package McStas is selected for its own flexibility. Since the characteristics of neutron beams generated from moderators make influence on the performance of pulse neutron spectrometers, it is important to perform the simulation with neutron source component written precisely. Both Energy dependence of neutron spectrum and time structure of neutrons were calculated using NMTC/JAERI97 and MCNP4a codes.The simulation parameters, which describe the pulse shape as a function of time, are optimized. The creation of neutron source components viewed to coupled H
with poisoned or unpoisoned for high resolution moderators. Monte Carlo simulations have turned out to be useful for design of neutron scattering instruments with high complexity. The software package McStas is selected for its own flexibility. Since the characteristics of neutron beams generated from moderators make influence on the performance of pulse neutron spectrometers, it is important to perform the simulation with neutron source component written precisely. Both Energy dependence of neutron spectrum and time structure of neutrons were calculated using NMTC/JAERI97 and MCNP4a codes.The simulation parameters, which describe the pulse shape as a function of time, are optimized. The creation of neutron source components viewed to coupled H moderator and viewed to decoupled H
moderator and viewed to decoupled H moderator of JSNS are reported.
moderator of JSNS are reported.
Katayama, Atsushi; Furukawa, Katsutoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo
Bunseki Kagaku, 52(6), p.461 - 467, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)An imaging ion detection system was introduced to a time-of-flight mass spectrometer (TOFMS) in order to increase dynamic range in the isotope ratio measurements. The new detection system utilizes a position sensitive micro channel plate (MCP) with a phosphor plate and a CCD camera which records light spots on the MCP. Mass discriminated ion beams produced by laser resonance ionization were swept on the surface of MCP by a time-depended electric field located in front of the MCP. The resulting light spots were recorded as images by CCD camera. A mass spectrum was obtained from the images. The present method was applied to the isotope analysis of calcium. A dynamic range of more than 5 orders of magnitude was achieved.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Ikeura, Hiromi*; Baba, Yuji
Surface Science, 532-535(1-3), p.1079 - 1084, 2003/06
Using a newly developed rotatable time-of-flight mass spectrometer(R-TOF-MS) and polarized synchrotron radiation, we have investigated orientation effect on fragmentation and desorption pathways occurring at the top-most layers of molecular solids. Reported will be polarization-angle dependencies of TOF mass spectra, high-resolution electron- and ion-NEXAFS in condensed formic acid, formamide and benzene. For condensed formamide(HCOND ), marked orientation effect was observed for the enhanced H
), marked orientation effect was observed for the enhanced H -yields following C1s
-yields following C1s 
 *
*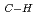 resonance. Direct photodissociation and charge-neutralization play an important role in the effect. For some fragment species, however, the bond scission showed no polarization dependence when dissociation sites were far from core-excited atoms. This is the case for N-D scission and D
resonance. Direct photodissociation and charge-neutralization play an important role in the effect. For some fragment species, however, the bond scission showed no polarization dependence when dissociation sites were far from core-excited atoms. This is the case for N-D scission and D -desorption following C1s excitation, suggesting that indirect process governs, where secondary electrons would induce the fragmentation.
-desorption following C1s excitation, suggesting that indirect process governs, where secondary electrons would induce the fragmentation.
Tamura, Itaru; Aizawa, Kazuya; Harada, Masahide; Shibata, Kaoru; Maekawa, Fujio; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi
JAERI-Research 2003-008, 34 Pages, 2003/03
Moderators components of the McStas code have been created for the design of JSNS instruments. Three cryogenic moderators are adopted in JSNS, One is coupled H moderators for high intensity experiments and other two are decoupled H
moderators for high intensity experiments and other two are decoupled H with poisoned or unpoisoned for high resolution moderators. Since the characteristics of neutron beams generated from moderators make influence on the performance of pulse neutron spectrometers, it is important to perform the Monte Carlo simulation with neutron source component written recisely. The neutron spectrum and time structure were calculated using NMTC/JAERI97 and MCNP4a codes. The simulation parameters, which describe the pulse shape over entire spectrum as a function of time, are optimized. In this paper, the creation of neutron source components for port No.16 viewed to coupled H
with poisoned or unpoisoned for high resolution moderators. Since the characteristics of neutron beams generated from moderators make influence on the performance of pulse neutron spectrometers, it is important to perform the Monte Carlo simulation with neutron source component written recisely. The neutron spectrum and time structure were calculated using NMTC/JAERI97 and MCNP4a codes. The simulation parameters, which describe the pulse shape over entire spectrum as a function of time, are optimized. In this paper, the creation of neutron source components for port No.16 viewed to coupled H moderator and for port No.11 viewed to decoupled H
moderator and for port No.11 viewed to decoupled H moderator of JSNS are reported.
moderator of JSNS are reported.
Shibata, Kaoru; Tamura, Itaru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi; Niimura, Nobuo
JAERI-Research 2002-036, 30 Pages, 2003/03
In this research report we describe the design of DYANA, a new neutron spectrometer dedicated for biology, biomaterials, and related soft-matter studies, which will be installed in the material and life science experimental facility project at the JAERI Tokai establishment. The DYANA spectrometer is an indirect-geometry crystal-analyzer instrument and it's energy and momentum transfer range are from several 10 eV to several meV and from 0.1
eV to several meV and from 0.1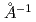 to several
to several 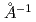 , respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
, respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kinouchi, Nobuyuki; Sakamoto, Ryuichi; Yoshida, Makoto
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(9), p.957 - 963, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:23.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)An anti-Compton spectrometer with semi-2 Compton suppression is designed to identify the photons emitted from low-level radioactive wastes from radioisotope usage and nuclear research laboratory. Since the objective sample is massive and large, the system has a full opening towards the sample position. The characteristics and features of the system concerning Compton suppression and reduction of the background component due to natural radioactive source are estimated by the Monte Carlo simulations. The anti-Compton technique is shown to be quite advantageous for the reduction of the surrounding natural background radiation, as well as the suppression of the background for the higher energy photons.
Compton suppression is designed to identify the photons emitted from low-level radioactive wastes from radioisotope usage and nuclear research laboratory. Since the objective sample is massive and large, the system has a full opening towards the sample position. The characteristics and features of the system concerning Compton suppression and reduction of the background component due to natural radioactive source are estimated by the Monte Carlo simulations. The anti-Compton technique is shown to be quite advantageous for the reduction of the surrounding natural background radiation, as well as the suppression of the background for the higher energy photons.
 detection system in the indoor environments of concrete buildings
detection system in the indoor environments of concrete buildingsTsutsumi, Masahiro; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kinouchi, Nobuyuki; Sakamoto, Ryuichi; Yoshida, Makoto
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(12), p.1109 - 1114, 2001/12
In order to predict the indoor background spectra to gamma detection systems, the gamma radiation field in a concrete building is studied by the Monte Carlo simulations. The parameters of wall thickness, room shape and dimensions were considered in the modeling. The indoor source geometry was simulated by a spherical layer model with the intention of easy and effective calculations. The model was applied to an unshielded germanium detector and the detection system with a more complex shielding configuration. As the results, we found that the indoor radiation field in concrete buildings can be predicted well with the source geometry of a spherical concrete layer of 25cm thickness and with the source of the natural major three components of the  U series,
U series,  Th series and
Th series and  K that are homogeneously distributed. The simulation model is useful for designing and optimizing gamma detection systems or shielding assemblies.
K that are homogeneously distributed. The simulation model is useful for designing and optimizing gamma detection systems or shielding assemblies.
Konno, Chikara; Maekawa, Fujio; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Uno, Yoshitomo; Kaneko, Junichi; Nishitani, Takeo; Wada, Masayuki*; Ikeda, Yujiro; Takeuchi, Hiroshi
Nuclear Fusion, 41(3), p.333 - 337, 2001/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Maekawa, Fujio; Wada, Masayuki*; Konno, Chikara; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Ikeda, Yujiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 51-52(Part.B), p.809 - 814, 2000/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English